
![]()
![]() Definitions of DK model and prevailing TM model
Definitions of DK model and prevailing TM model
![]() Problems with TM model
Problems with TM model
![]() Feature and Construction of DK model
Feature and Construction of DK model
![]() Comparison between DK model and TM model
Comparison between DK model and TM model
![]() Absolute Employee Evaluation
Absolute Employee Evaluation
![]() Retirement pay system revitalizing both a company and its employees
Retirement pay system revitalizing both a company and its employees
![]() Definitions of DK model and prevailing TM model
Definitions of DK model and prevailing TM model
<DK MODEL>
DK model is a wage structure with the flexible DYNAMIC (or DOTAITEKI) which corresponds to the different environmental changes. It has KAISO (layered) structure of absolute amounts linked to job, job-performing ability and performance.
It uses the Absolute Employee Evaluation by performance, which develops human resources.
<TM MODEL>
TM model is a prevailing wage structure which accumulates (TSU-MIAGE) the periodic (yearly) wage increases on the basic wage (starting wage) on the preceding year.
TM model determines the wage increases by the Comparative Employee Evaluation which the personal qualities and performances of employees are rated comparatively within a group.
Click Here to go back to the top.
![]() Problems with TM model
Problems with TM model
TM model has come to face with problems, which are inherent in the
system under low economic growth and rapid aging. The system became
unable to meet the growing demand of employees 'equal pay for equal
work'. Also, the very bases on which the system rested - a work force
with a lower median age, fewer employees with higher education,
collective and seniority oriented value sharing among the employees -
have changed.
The most fundamental problem with this system is the possible lead
to the company’s financial imbalance due to the automatic increase of
the employees age and the labor costs to disproportional employees'
abilities or performances.
If wage increase by TM model is kept on for several years, it would
swallow up the majority of an average company's operating profits
unless added value can be increased enough to offset it.
Another defect inherent in TM model is its lack of rational basis
for determining individual wages. This lack of rational basis in
determining wages or wage increases leads to the conflict of interests
between the company and the employees in setting the wages or increases.
In addition, the amount of retirement payment increases like a
snowball under TM model, which will cause financial imbalance of a
company and make the situation seriously fatal.
All of those findings show that TM model is in compelling need for drastic changes.
Click Here to go back to the top.
![]() Feature and Construction of DK model
Feature and Construction of DK model
<Feature of DK model>
●The system can cope with the environmental changes
─ 'Rapid aging of population', 'IT revolution' and 'Mature economy'.
●The system can secure a company's viability and the continued payment of
the wages.
●The system has three guidelines for determining wages,
─ 'Maintenance of appropriate wage level', 'Securing fair wage differentiation
among employees',
and 'Certainty through establishing wage rules'.
●The system directly employs the methods of 'absolute' (non-comparative)
employee evaluation,
which is able to promote the employees' training to keep the teamwork.
●The company can induct the system easily.
<Outline of DK model>
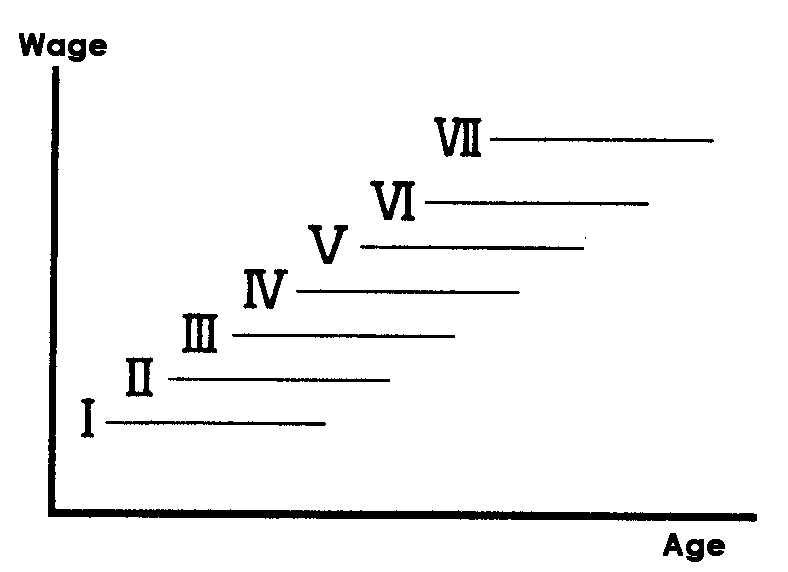
1.Job Grading(Ⅰ~Ⅶ):Grade
The range wage rates are set forth primarily by the job responsibility (as graded).
 |
2.Sub-grading(①~⑤):Class
The actual rates are given for each job-performing ability levels (as sub-graded) within each job grade.
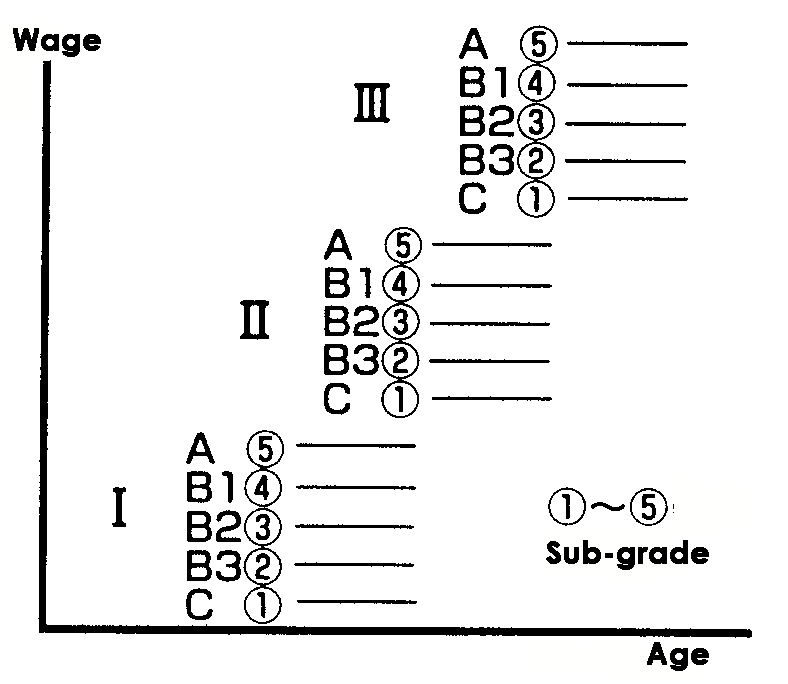 |
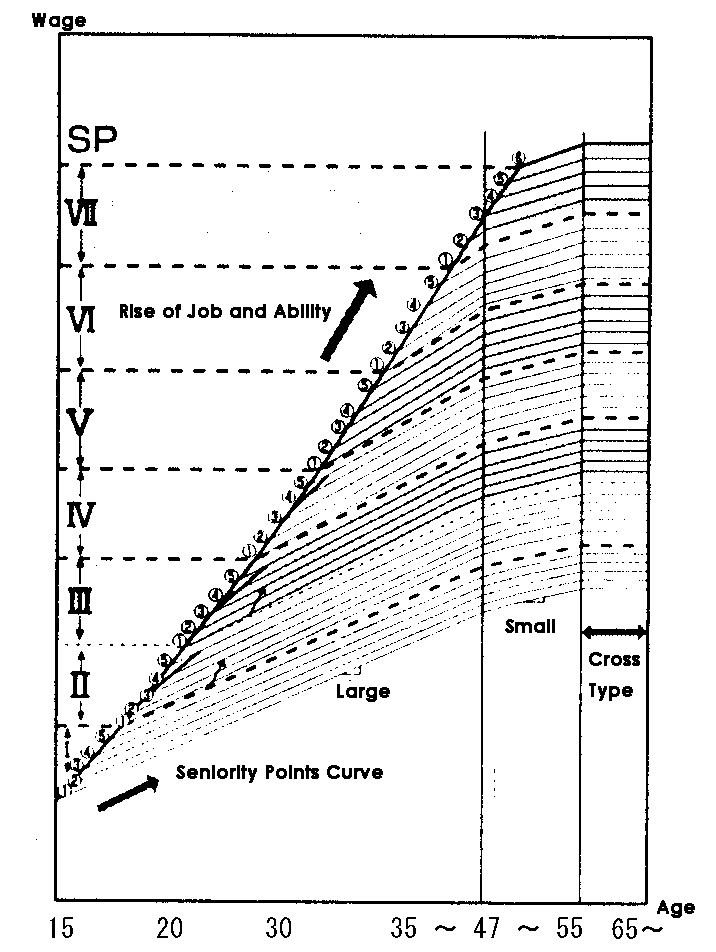
3.Seniority Factor :Number
Just as belonging to the main trunk as branches do, seniority merit
increases are limitedly attached, to secure the living costs.
 |
4.By integrating 1~3, the basic wage structure is obtained.
This system "DK model" can select any wage levels to each of job grade,
ability sub-grade and seniority merits, making the structure very
flexible both for individual and total wage administration.
 |
Click Here to go back to the top.
![]() Comparison between DK model and TM model
Comparison between DK model and TM model
| DK model | TM model | |
| Effects on Employees' consciousness | Clear employees' position, providing employees with high spirit and security | Lack of rationales in determining wage, giving employees anxiety |
| Treatment for Mid-career hiring employees | Fair treatment for employees | Standard is set for the new graduates, needing adjustment |
| Treatment for Less aged employees | Fair treatment for employees | Unfair treatment for employees |
| Effects on Personnel evaluation | Able to give feedback to the employees, using the absolute employee evaluation | Unopened evaluation |
| Effects on human recourses development | Promotes challengers | Not promotes challengers |
| Effects on Business management | High added value productivity, reflecting the corporate earnings on the management | Do not reflect the corporate earnings on the management |
| Realization of Company's vision | Connecting directly with the realization of the company's vision | Not connecting with the realization of the company's vision |
| Rate of Self-realization | High | Low |
Click Here to go back to the top.
![]() Absolute Employee Evaluation
Absolute Employee Evaluation
<Problems with Comparative Employee Evaluation>
●The evaluation might tend to be subjective depending on the managers who
make evaluation.
This would cause unfairness and possible overpayment or underpayment of the company.
●As employees know that they are evaluated
comparatively among fellow workers, they might well tend to focus their
efforts on the relative competition with each other, often steering
their behaviors to earn subjective favor from their managers.
●Both the employees and managers are deprived of concrete standards for
the employees to strive for, and for the managers to guide with.
All those things could cause the crippling of morale in the depth
of minds and subsequent erosion of real organization effectiveness.
<Absolute Employee Evaluation>
Determination of wage and wage increase is certainly one of the primary
purposes of employee evaluation. However, evaluation should not be
confined to this role alone but should also serve the broader purposes
of improving and developing employees' personal qualities such as
attitude, knowledge, ability and ultimately the pursuit of the
company's better performance through the maturity of these factors and
the needed managerial countermeasures that are found through the
evaluation.
In order to meet the above purposes, it is necessary that the
following factors and procedures are integratedly considered and
arranged.
・Right assessment of the employee's personal qualities such as
aptitudes, knowledge, experience, ability and desire / expectation
・Right recruitment and assignment
・Job description
・Tangible standards for job-performing ability requirements
・Absolute and concrete evaluation items and standards
・Provision for right guidance, instruction / information, coaching /
development and motivation that inspire employees for higher attainment
・Evaluation
・Counseling for under attainment and improvement
・Reflection and actions on the manager's side for improvement
●Evaluation points
・Attitude should be weighted more than ability and results for the employees in elementary grade.
・For middle career employees, ability should be weighted more than attitude and result.
・For managers, results should be weighted more than attitude and ability.
<Comparison between Absolute Employee Evaluation and Comparative Employee
Evaluation>
| Viewpoint | Absolute Employee Evaluation | Comparative Employee Evaluation |
| Definition | Competition with the objectives | Competition with other employees |
| Consensus | Linking to the standard of job and the standard requirements of work competence, Easy to get the consensus of the evaluator and the evaluee |
Not linking to the standard of job and the standard requirements of work competence, uneasy to get the consensus of the evaluator and the evaluee |
| Linking to Corporate earnings | Evaluation standard linking to the corporate earnings | Evaluation standard not linking to the corporate earnings |
| Quality of Target | Brings employees' high spirits and the raise of the corporate earnings by the clear target | Does not bring employees' high spirits and the raise of the corporate earnings by the vague target |
| Human resource development | Makes each employee's weak points and strong points clear, and gives the target for the defeated employees to revive | Brings the competition with employees, but not the human resource development |
| Teamwork | Brings the good teamwork to attain the goal | Brings hostilities and the endless race among employees for always dividing employees by SABCD in spite of high employees' ability |
| Structure | Does not use the regular distribution | Uses the regular distribution to decide the rate of SABCD |
| Uses evaluation items and standards suiting to the company and the workplace | Does not use the concrete evaluation items | |
| Decides the weight of each job grade and each evaluation item | Does not decide the weight of each evaluation item | |
| Practice | Does not need to use C, if employees attain B | Always uses SABCD to divide employees |
| Possible to evaluate one employee | Not possible to evaluate one employee | |
| Easy adjustment of the evaluation by the clear standard | Uneasy adjustment of the evaluation by the comparison among employees |
Click Here to go back to the top.
![]() Retirement pay system revitalizing both a company and its employees
Retirement pay system revitalizing both a company and its employees
The prevailing lump-sum retirement payment under seniority based pay system is calculated as
[The monthly basic wage rate at the time of retirement]×[The rate of
length of service]×[The rate of the reason for retirement].
Since the wage rate and length of service include seniority factor, the
amount of retirement payment increases like snowball, which will cause
financial imbalance of a company.
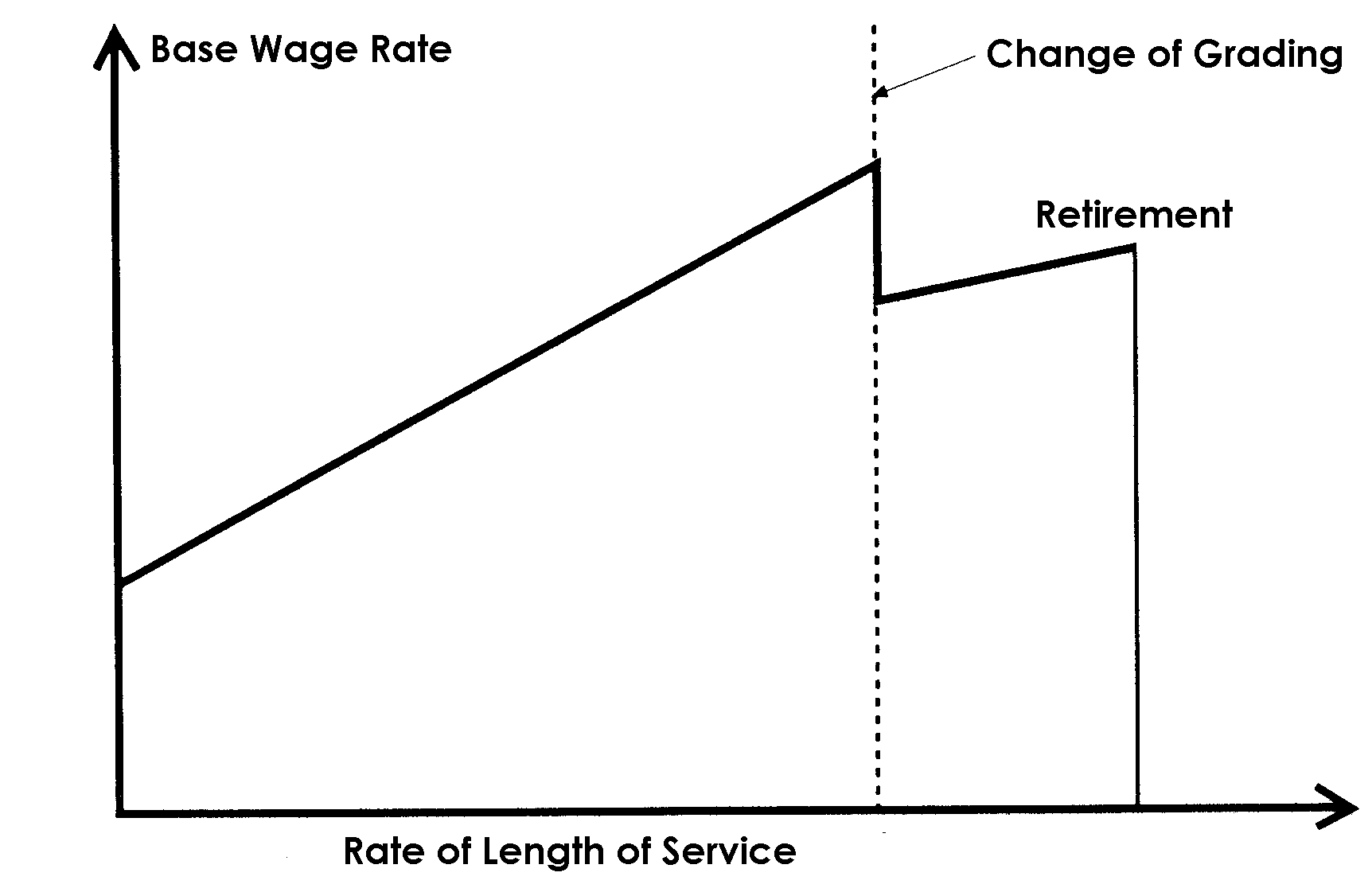
According to the basic concept of the new system, the base wage rate for calculating retirement payment is determined separately
from the monthly basic wage rate.
The base wage rate for calculating retirement payment is determined
basically by employee's performance and the rate to secure the cost of
post retirement living which is added to the retirement payment.
The retirement payment is calculated by the cumulative area, the
base wage rate times the rate of length of service, regardless of the
changing grade.
  |